Unit 10 : Experimental Physics
Measurement of fundamental constants: e, h, c – Measurement of high and low resistances,
L and C
Detection of X-rays, gamma rays, charged, particles, neutrons etc – lionization
Detection of X-rays, gamma rays, charged, particles, neutrons etc – lionization
chamber – proportional counter –GM counter – Scintillation detectors – Solid state detectors
Ionization chamber
The ionization chamber used to measure the average number of ionizations per minute occurring within the gas. It is a gas-filled can (air) with a window at one end, two parallel plates (anode& cathode), a meter, and a battery.
The gas is most often at normal atmospheric pressure. A thin window at one end of the can admits radiation which ionizes the air. The current is measured by meter which is connected as shown the circuit.
Proportional counter
The proportional counter is similar to an ionization chamber. The filling gas is more likely to be argon or an argon–methane mixture than air, but the major difference between them is the higher voltage and the resulting gas amplification.
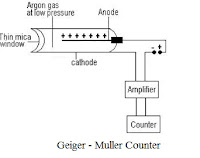
GM counter
The Geiger counter is an ionization chamber that operates at a relatively high applied voltage The chamber is usually filled with argon containing traces of other gases such as halogen or methane, although a detector will function with a filling as simple as dry air. The sensitive end of the probe is generally a mica window protected by an external metal mesh. When the radioactive radiations enter the GM tube through the mica window and ionises the argon gas. A pulse current is produced and counted by a counter.
Scintillation detectors
Scintillation detectors consist of a phosphor-coated screen and a photomultiplier tube. Radiation incident upon the phosphor produce photons in the ultraviolet part of the spectrum, which are amplified by the Photo Multiplier tube then output signal is fed to the electronic circuits.
The semiconductor detector most commonly used in the detection of gamma radiation is the germanium–lithium detector. This type of detector has been used in gamma radiation spectroscopy since the 1960.
Semiconductor detector has a PN junction with reverse bias. The interaction of Radiation with the semiconducting junction produces electron-hole pairs. These pairs are pulled by the electric field and that can be identified with proper electronics circuit.
Emission and absorption spectroscopy – Measurement of magnetic field. Hall
effect – Magnetoresistance – X-ray and neutron diffraction – Vacuum techniques – Basic
idea of conductance – Pumping speed etc- Pumps: Mechanical pump – Diffusion pump –
Gauges: Thermocouple – Penning – Pirani – Hot cathode – Low temperature: cooling a
sample over a range upto 4 K and measurement of temperature – Error analysis and
hypothesis testing – Propagation of errors – Plotting of graph - Distributions – Least squares
fitting - Criteria for goodness of fits – Chi square test.